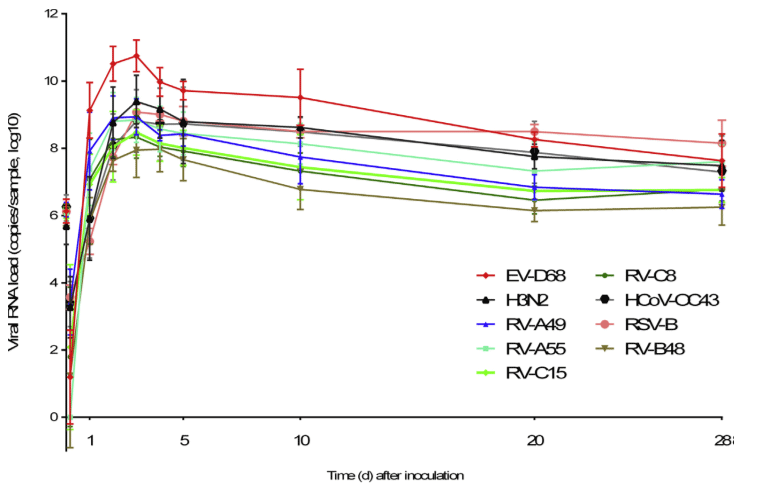
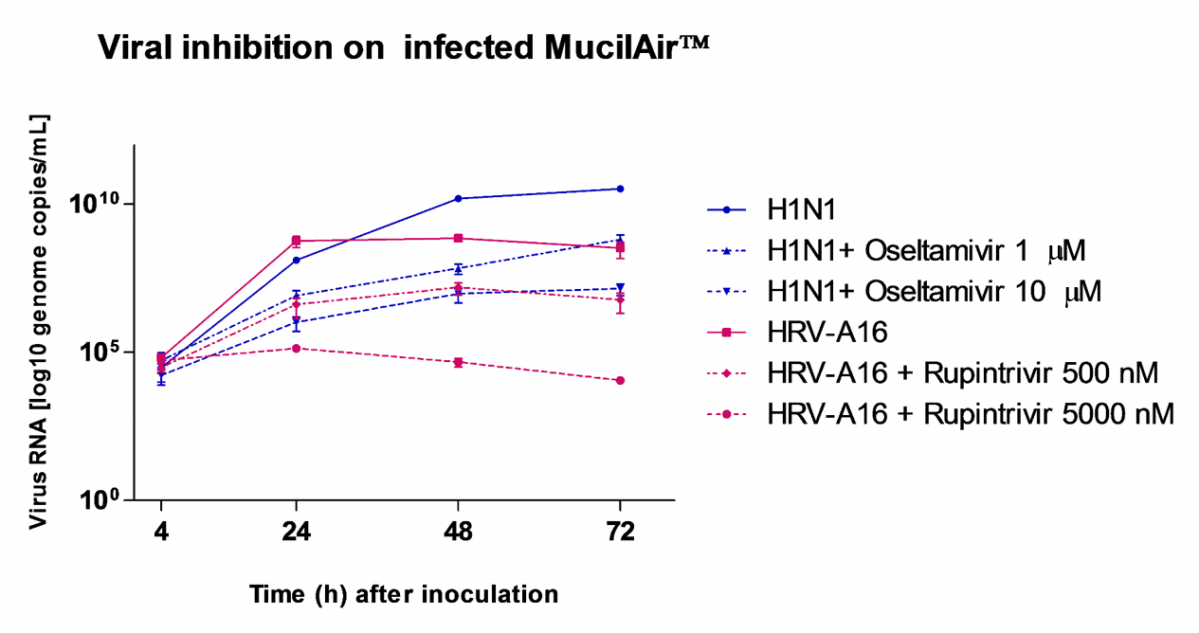
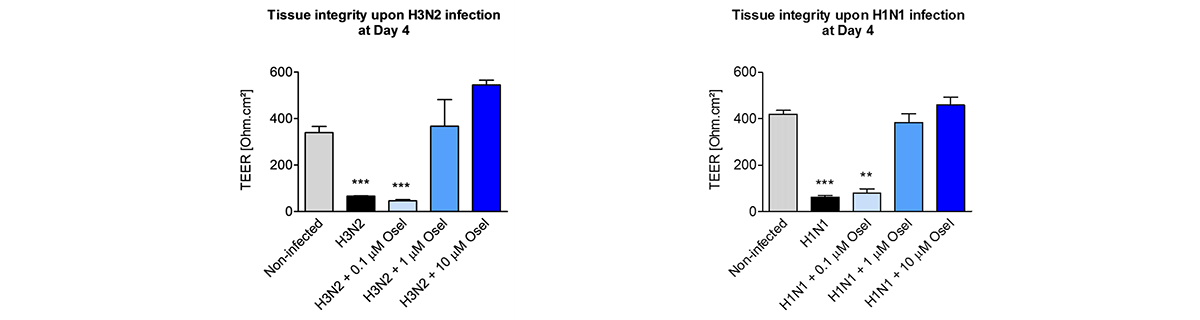
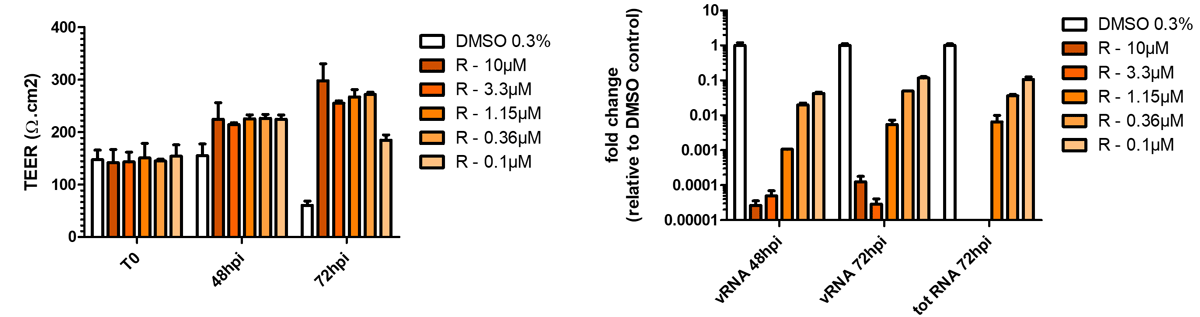
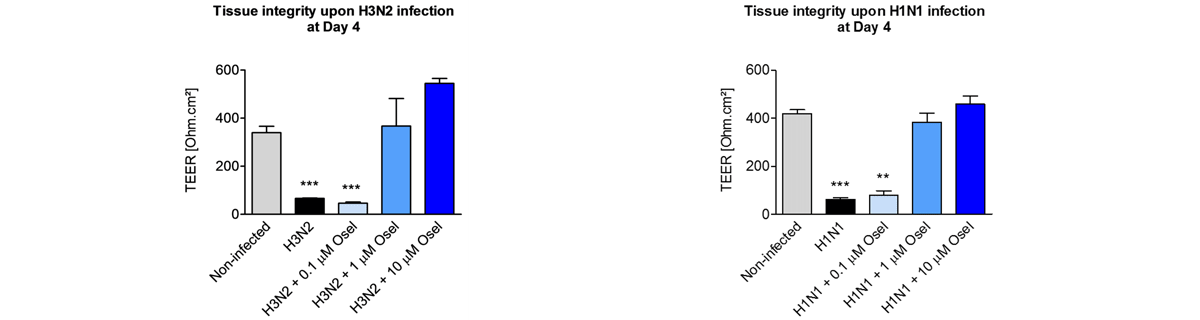
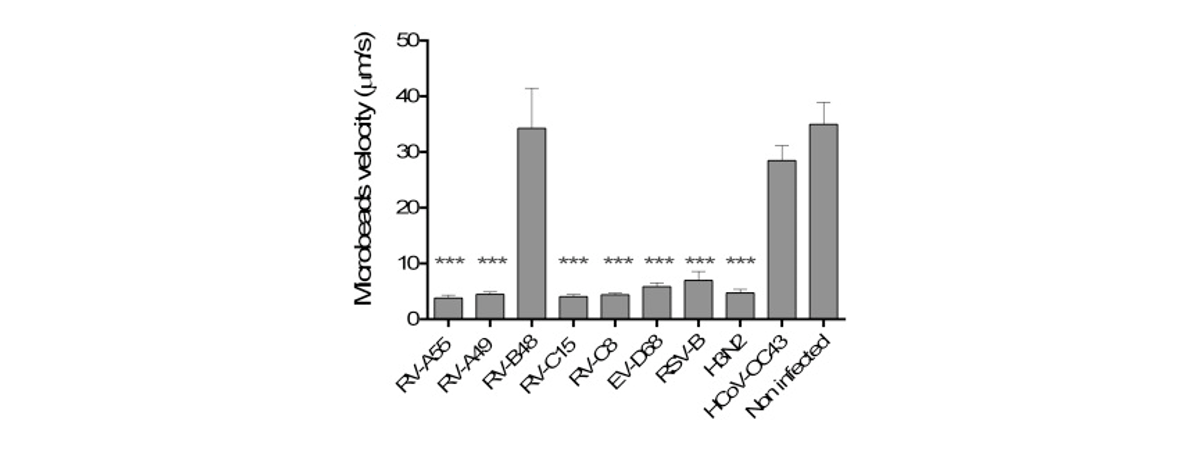
Respiratory viral infections cause mild to severe diseases worldwide, such as common cold, bronchiolitis and pneumonia and are associated with huge costs for society.
Relevant human models are mandatory to test new molecules for shortening and alleviating these diseases, or to develop new therapies.
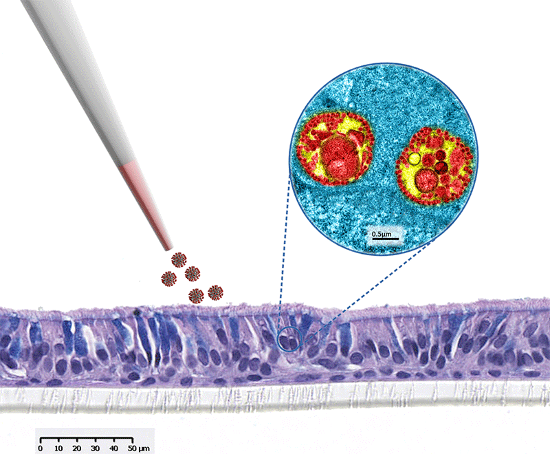
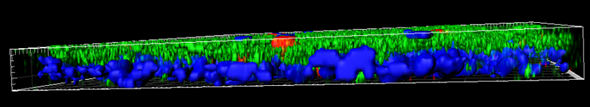
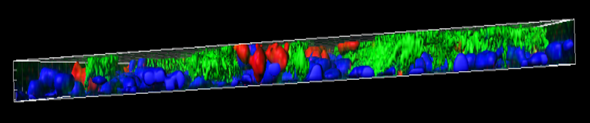
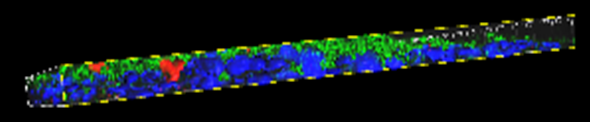
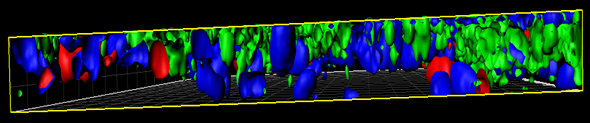
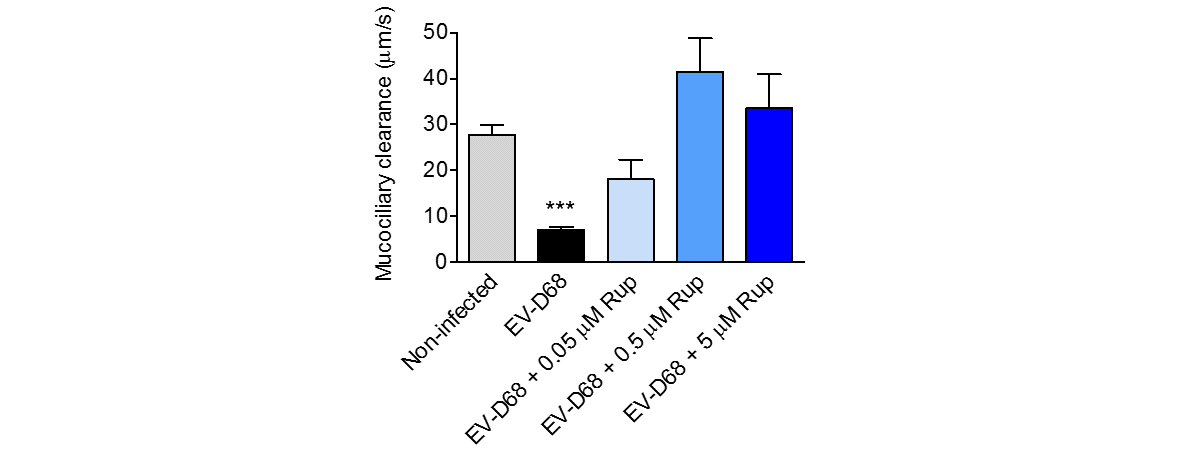
MucilAir™, SmallAir™ and AlveolAir™, holds in vitro specific mechanisms to counter invaders comparable to the in vivo situation, such as mucus production, mucociliary clearance, and secretion of defensive molecules.